NOTE: If you have any queries regarding the solutions, feel free to comment down.
1. 3.1: Simplify the following boolean functions using three-variable maps:
a) a. F(x,y,z)=∑(0,1,5,7)
Solution:-
b) F(x,y,z)=∑(1,2,3,6,7)
Solution:-
Therefore, F=x’z+y
c) F(x,y,z)=∑(3,5,6,7)
Therefore, F=xy+yz+xz.
d) F(A,B,C) =∑(0,2,3,4,6)
F=C’+A’B
Solution:-
b. x’y’+yz+ x’yz’
Therefore, F= x’+yz
c. A’B+BC’+B’C’
F=C’+A’B
a. F(A,B,C,D)=∑(4,6,7,15)
Therefore, F=A’BD’+BCD

F= wx+w’x’y
c. F(A,B,C,D)=∑(3,7,11,13,14,15)
F=CD+ABD+ABC
3.4. Simplify the following Boolean functions using four variable
maps:
a. F(w,x,y,z)=∑(1,4,5,6,12,14,15)
F=xz’+w’y’z+wxy
F=A’B’D’+A’C’+BCD+ACD

F=BD+B’D’+A’D’
3.5. Simplify the following Boolean expressions using four-variable
maps:
a. w’z+xz+x’y+wx’z
F=z+x’y
b. B’D+A’BC’+AB’C+ABC’
F=BC’+B’D+AB’C
c. AB’C+B’C’D’+BCD+ACD’+A’B’C+A’BC’D
F=B’D’+CD+AC+A’BD
F=x’y+wy+xz
3.6. Find the minterms of following Boolean expressions by first
plotting each function in a map:
a) xy+yz+xy’z
|
|
yz |
|
|
|
|
|
x |
|
00 |
01 |
11 |
10 |
|
|
0 |
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
1 |
|
1 |
1 |
1 |
b. CD’+ABC’+ABD’+A’B’D
|
|
CD |
|
|
|
|
|
AB |
|
00 |
01 |
11 |
10 |
|
|
00 |
|
1 |
1 |
1 |
|
|
01 |
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
11 |
1 |
1 |
|
1 |
|
|
10 |
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
yz |
|
|
|
|
|
wx |
|
00 |
01 |
11 |
10 |
|
|
00 |
1 |
|
|
1 |
|
|
01 |
|
1 |
1 |
|
|
|
11 |
|
|
1 |
1 |
|
|
10 |
1 |
|
|
1 |
3.7. Simplify the following Boolean expressions by first finding the
essential prime implicants.
a. F(w,x,y,z)=∑(0,2,4,5,6,7,8,10,13,15)
F=xz+x’z’+w’x
b. F(A,B,C,D)=∑(0,2,3,5,7,8,10,11,14,15)
The essential prime implicants are AC, B’D’,A’BD
F=AC+B’D’+A’BD+CD
c. F(A,B,C,D)=∑(1,3,4,5,10,11,12,13,14,15)
The essential prime implicants are BC’ and AC
F=BC’+AC+A’B’D
3.8. Simplify the following Boolean functions using five-variable
maps:
a. F(A,B,C,D,E)=∑(0,1,4,5,16,17,21,25,29)
F=A’B’D’+AD’E+B’C’D’
F=A’B’C+DE+B’C’E’
F=D’E’+B’D’
3.9. Simplify the following Boolean functions in product of sum:
a. F(w,x,y,z)=∑(0,2,5,6,7,8,10)
F’=x’z+wx+xy’z’
F=(x+z’)(w’+x’)(x’+y+z)
b. F(A,B,C,D)=∏(1,3,5,7,13,15)
F’=A’D+BD
F=(A+D’)(B’+D’)
c. F(x,y,z)=∑(2,3,6,7)
F’=y’
F=y
d. F(A,B,C,D)=∏(0,1,2,3,4,10,11)
F’=B’C+A’B’+A’C’D’
F=(B+C’)(A+B)(A+C+D)
3.10. Simplify the following expressions in (i)sum of products
(ii)products of products:
a. x’z’+y’z’+yz’+xy
F=xy+z’
F’=y’z+x’z
F=(y+z’)(x+z’)
F=AC’+CD+A’D
F’=CD’+A’D’+A’BC’
F=(C’+D)(A+D)(A+B’+C)
c. (A’+B’+D’)(A+B’+C’)(A’+B+D’)(B+C’+D’)
F=AD’+A’C’
F’=AD+C’D’+A’BC
F=(A’+D’)(C+D)(A+B’+C’)
3.11. Draw the AND-OR gate implementation of the following function after simplifying it in (a)sum of products and (b) product of sums:
F(A,B,C,D)=∑(0,2,5,6,7,8,10)
F=B’D’+A’BD+A’BC
F’=B’D+AB+BC’D’
F=(B+D’)(A’+B’)(B’+C+D)
3.12. Simplify the following expressions and implement them with two-level NAND gate circuits:
a. AB’+ABD+ABD’+A’C’D’+A’BC’
F=A+BC’+C’D’
b. BD+BCD’+AB’C’D’
BD+BC+AB’C’D’
3.13. Draw a NAND logic diagram that implements the complements of the following function:
F(A,B,C,D)=∑(0,1,2,3,4,8,9,12)
F’=BD+BC+AC
3.14. Draw a logic diagram using only two-input NAND gates to
implement the following
expression:
(AB+A’B’)(CD’+C’D)
3.15. Simplify the following functions and implement them with
two-level NOR gate circuits:
a. F=wx’+y’z’+w’yz’
F’=w’z+xz+wxy
F=(w+z’)(x’+z’)(w’+x’+y’)
b. F=(w,x,y,z)=∑(5,6,9,10)
F’=w’x’+wx+y’z’+yz
F=(w+x)(w’+x’)(y+z)(y’+z’)
3.16. Implement the functions of problem 15 with three level NOR
gate circuits
a. F=wx’+y’z’+w’yz’
F’=(w’+x)(y+z)(w+y’+z)
And F=(F’)’
b. F=(w,x,y,z)=∑(5,6,9,10)
|
|
yz |
|
|
|
|
|
wx |
|
00 |
01 |
11 |
10 |
|
|
00 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
01 |
|
1 |
|
1 |
|
|
11 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
10 |
|
1 |
|
1 |
F=w’xy’z+w’xyz’+wx’y’z+wx’yz’
F’=(w+x’+y+z’)(w+x’+y’+z)(w’+x+y+z’)(w’+x+y’+z)
a. F=AB’+ABD+ABD’+A’C’D’+A’BC’
F’=A’C+A’B’D
F=(F’)’
b. F=BD+BCD’+AB’C’D’
F’=B’C+B’D+A’C’D’+BC’D’
3.18. Give three possible ways to express the function F with eight
or fewer literals
F(A,B,C,D)=∑(0,2,5,7,10,13)
F=A’B’D’+B’CD’+A’BD+BC’D
F=B’D’(A+C)+BD(A’+C’) (1ST
WAY)
F’=BD’+B’D+ABC+AB’C’
=B(D’+AC)+B’(D+AC’)
F=(B’+D(A’+C’))+(B+D’(A’+C)) (2ND WAY)
=D’(B+AC’)+D(B’+AC)
F=(D+B’(A’+C))(D’+B(A’+C’)) (3RD
WAY)
3.19. Find eight different two level gates circuits to implement F=xy’z+x’yz+w
F=w+x’yz+xy’z
AND-OR implementation
NAND –NAND implementation
F’=w’z’+w’x’y’+w’xy
F=(w+z)(w+x+y)(w+x’+y’)
OR-AND implementation
NOR-NOR implementation
F=xy’z+x’yz+w
F=((x’+y+z’)(x+y’+z’)(w’))’
NOR-OR implementation
OR-NAND
F’=w’z’+w’x’y’+w’xy
F=(w’z’+w’x’y’+w’xy)’
NAND-AND implementation
AND-NOR implementation
3.20: implement the function F with the following two level forms- NAND-AND, AND-NOR, OR-NAND, NOR-OR.
F(A,B,C,D)=m0+m1+m2+m3+m4+m8+m9+m12
F=C’D’+A’B’+B’C’
F=((C+D)(A+B)(B+C))’
F’=AC+BC+BD
F=(A’+C’)(B’+C’)(B’+D’)
F=(AC+BC+BD)’
NAND-AND
AND-NOR
OR-NAND
NOR-OR
3.21:
List the eight degenerate two level forms and show that they reduce to a single
operation. Explain how the degenerate two level forms can be used to extend the
number of inputs to a gate.
AND-OR
OR-AND
NAND-NAND
NOR-NOR
NOR-OR
NAND-AND
OR-NAND
AND-NOR
The degenerate two level forms can be used to extend the number of inputs to a gate as using these forms we can get a single operation effectively.
3.22:
Simplify the Boolean function F together with the don’t care conditions d, then
express the simplified function in sum of minterms.
a)
F(x,y,z)=m0+m1+m2+m4+m5
d(x,y,z)=d3+d6+d7
F=1
F=m0+m1+m2+m3+m4+m5+m6+m7
b)F(A,B,C,D)=m0+m6+m8+m13+m14
d(A,B,C,D)=d2+d4+d10
F=B’D’+CD’+ABC’D
F=m0+m2+m6+m8+m13+m14
c)
F(A,B,C,D)=m1+m3+m5+m7+m9+m15
d(A,B,C,D)=d4+d6+d12+d13
F=C’D+BD+A’D
F=m1+m3+m5+m7+m9+m13+m14
3.23: Simplify the Boolean function F together with the don’t care conditions d (i) sum of products
(ii)
product of sum
a) F(w,x,y,z)= m0+m1+m2+m3+m7+m8+m10
d(w,x,y,z)=d5+d6+d11+d15
F=x’z’+w’z
F’=xz’+wz
F=(x’+z)(w’+z’)
b) b) F(A,B,C,D)=m3+m4+m13+m15
d(A,B,C,D)= d1+d2+d5+d6+d8+d10+d12+d14
F=BD’+AB+A’B’D
F’=B’D’+AB’+A’BD
F=(B+D)(A’+B)(A+B’+D’)
3.24: A logic circuit implement the following Boolean function F=A’C+AC’D’
It
is found that the circuit input combination A=C=1 can never occur. Find a
simpler expression for F using the proper don’t care conditions.
Solution:
The don’t care terms will be d=AC
F=C+AD’
3.25:
Implement the following Boolean function F together with the don’t care conditions d using no more than two
NOR gates. Assume that both the normal and complement inputs are available.
F(A,B,C,D)=(m0+m1+m2+m9+m11)
d(A,B,C,D)=(d8+d10+d14+d15)
F’=B+A’CD
F=B’(A+C’+D’)
3.26:
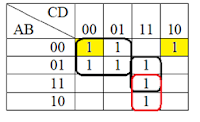
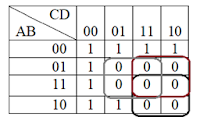
Simplify the following Boolean function using the map presented in Fig : 3.30(a)
and repeat using the map of figure 3:30(b)
F(A,B,C,D)=m1+m2+m3+m5+m7+m9+m10+m11+m13+m15
F=D+BC'
F=D+BC'














































































0 Comments